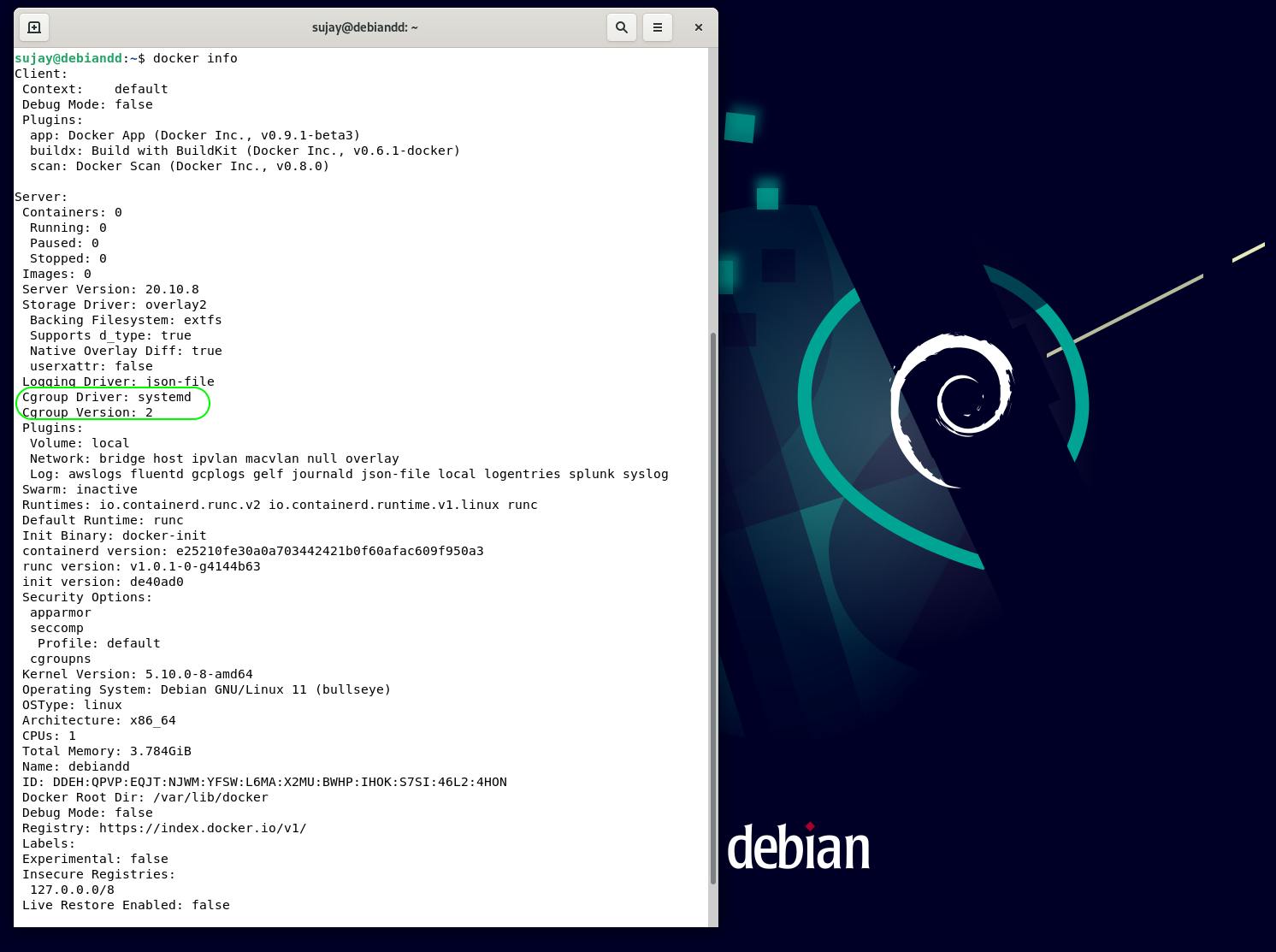
Debian 11 "bullseye" was released on 14th August 2021. In this blog, we will go through the steps of installing docker on this new release of Debian.
Installing Docker Engine for the first time on a new Linux host machine requires you to set up the Docker repository for you to install and update Docker.
Setting up the repository
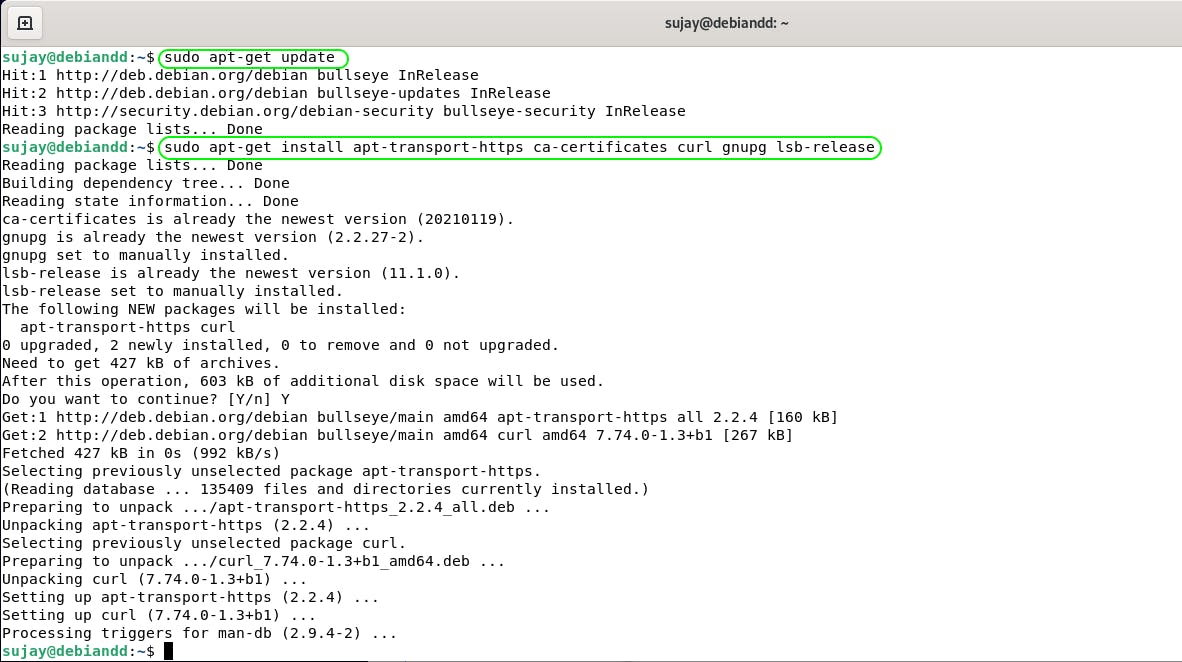
Update the apt package index and install the below packages to allow apt to use a repository over https.
$ sudo apt-get update
$ sudo apt-get install \
apt-transport-https \
ca-certificates \
curl \
gnupg \
lsb-release
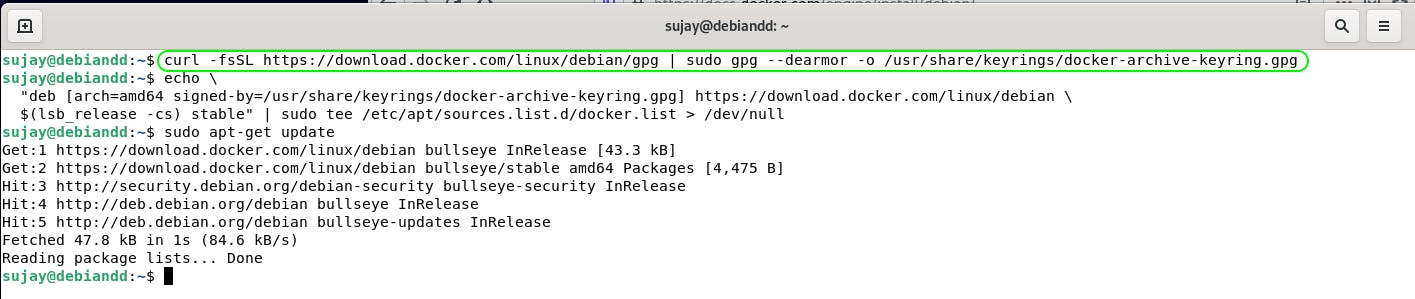
Add Docker’s official GPG key:
$ curl -fsSL https://download.docker.com/linux/debian/gpg | sudo gpg --dearmor -o /usr/share/keyrings/docker-archive-keyring.gpg
Use the following command to set up the stable repository.
echo \
"deb [arch=amd64 signed-by=/usr/share/keyrings/docker-archive-keyring.gpg] https://download.docker.com/linux/debian \
$(lsb_release -cs) stable" | sudo tee /etc/apt/sources.list.d/docker.list > /dev/null
Also update the apt package index using
sudo apt-get update
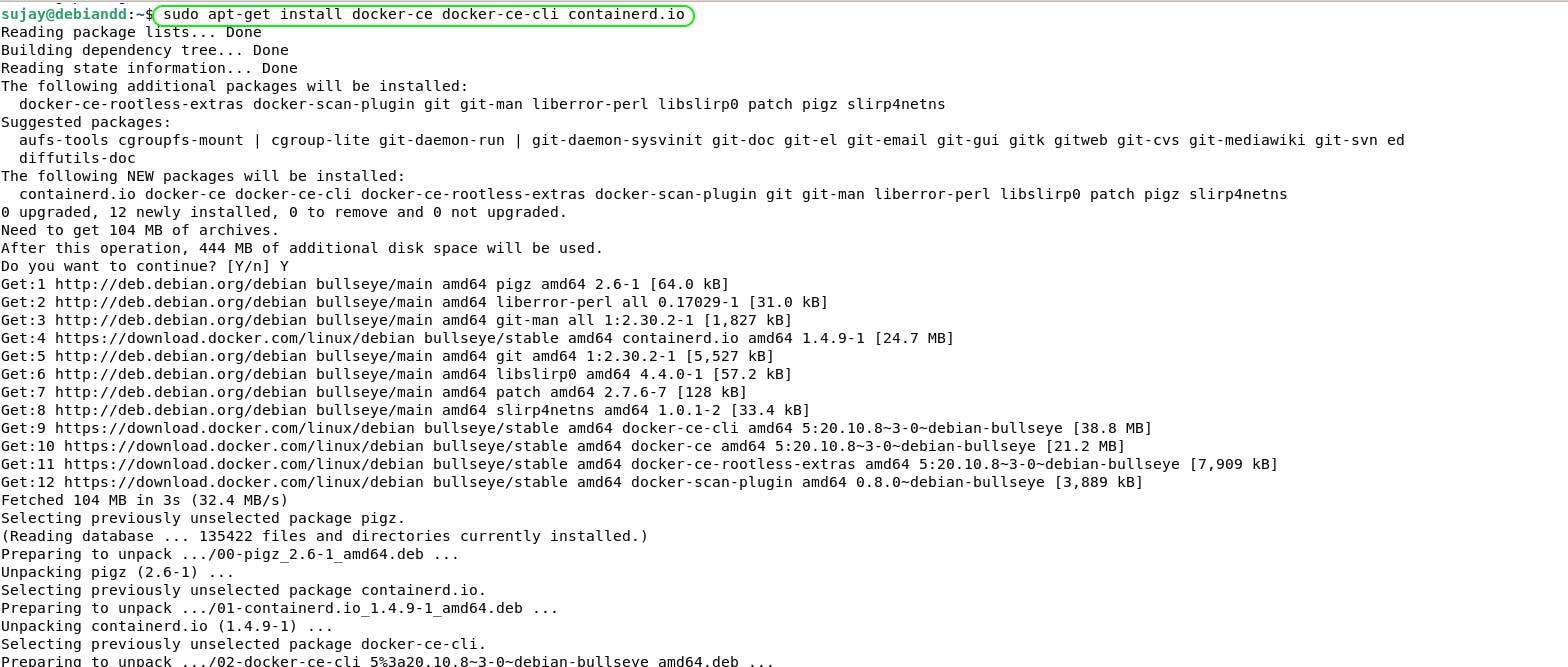
Install Docker Engine
$ sudo apt-get install docker-ce docker-ce-cli containerd.io
Once the installation is finished you may run the docker command - docker version to see the latest docker installed on your new Debian 11 machine.
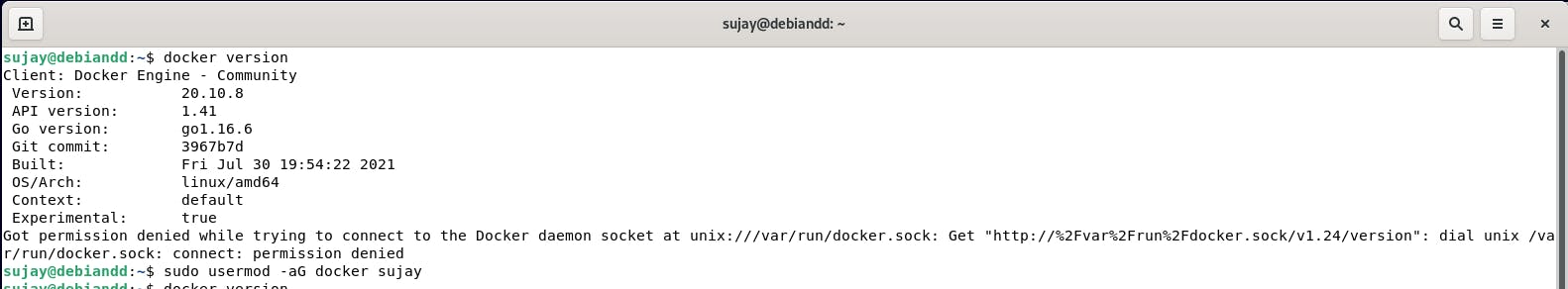
At this moment you should see an error connecting to the docker daemon through CLI which is due to the reason the current user doesn't have enough permission. This can be resolved with the below command:
sudo usermod -a -G docker $USER
The
dockergroup grants privileges equivalent to the root user. Check Docker daemon attack surface to see how this impacts security in your system.
To provide users with a unified resource-control hierarchy, systemd now defaults to using control groups v2 (cgroupv2) which got supported in Docker Engine 20.10.